How to Fix the Video Not Playing Issue in Windows (Codec Not Supported, Need New Codec). Watching videos on your Windows computer can sometimes hit a snag, especially when the video fails to play, showing an error like “The video cannot be played, (Codec Not Supported, Need New Codec)” or it simply doesn’t load. This issue often arises due to missing or incompatible video codecs.
It’s a frustrating experience, to say the least. But fear not, dear reader, for I’m here to guide you through the process of fixing those pesky video playback issues. In this article I will show you How to Fix the “Video Not Playing” Issue in Windows (Codec Not Supported, Need New Codec), Before diving into technical fixes lets learn something about the reason, codec, etc.
What is Codec? What does a Codec do?
A codec is a software component that enables the compression and decompression of digital data, such as audio and video files. A codec performs two main functions.
Compression: A codec compresses digital data to reduce its size, making it easier to store and transmit.
Decompression: A codec decompresses the compressed data, restoring it to its original form, so it can be played back or edited.
Here is a simple explanation of how a codec actually works:
The process starts with data capture, where audio or video data is recorded or ingested into a device. The captured data is then compressed using a codec. Compression reduces the size of the data, making it easier to store and transmit. The compressed data is then encoded into a digital format using an encoding algorithm. This algorithm converts the data into a binary code. The encoded data is then transmitted over a network or stored on a device. When the data is received or retrieved, it is decoded using a decoding algorithm. This algorithm converts the binary code back into its original form. The decoded data is then decompressed, restoring it to its original size and quality. Finally, the decompressed data is played back, allowing users to view or listen to the audio or video content.
How to Fix the Video Not Playing Issue in Windows (Codec Not Supported, Need New Codec)
The video not playing issue on Windows is usually caused by missing or incompatible codecs, an outdated graphics driver, or a faulty media player. By following these methods, you can troubleshoot and resolve the issue. Start by checking your media player, installing missing codecs, updating your drivers, and ensuring that your system is up to date. If the problem persists, consider converting the video to a more widely supported format. With these methods, you should be back to enjoying your videos without interruptions.
Method 1: Download and Install the Required Codec
Select the video file and right click on it, click on Open with and select Film & TV, a dialogue box appears, then click on Get it. When you click on get it micro soft office opens automatically, then click on Get to Install codec extension, and then click on Open.
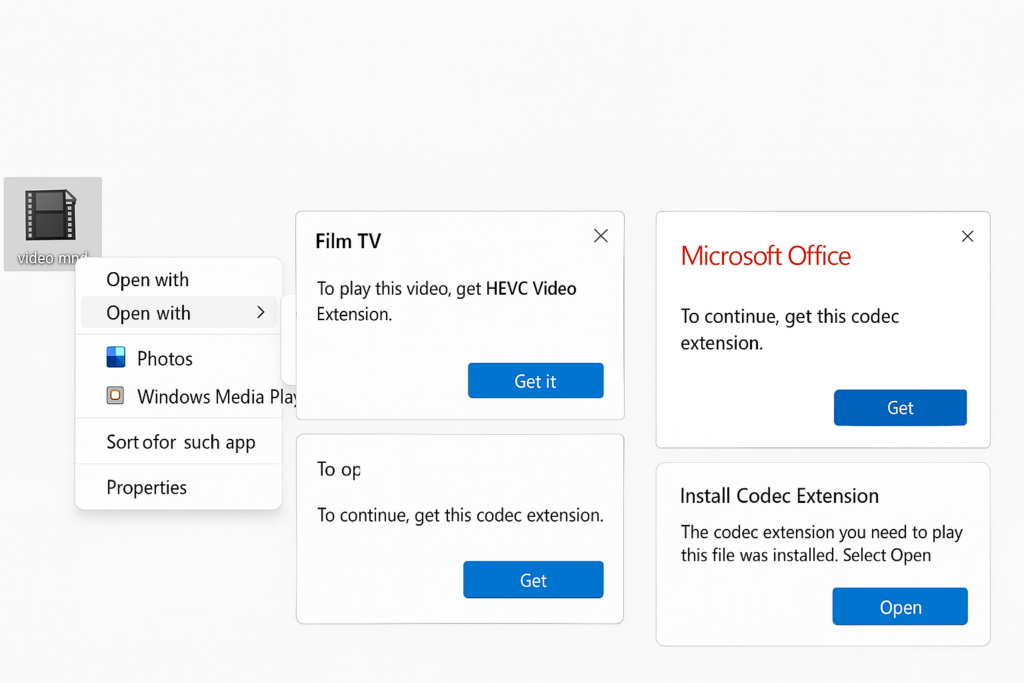
It’s time to test the video. Open your video player and try playing the video again. If everything is configured correctly, the video should play smoothly.
Method 2: Update Your Graphics Drivers
Right-click on the Start menu and select Device Manager, expand the Display adapters section, then right click on your Graphics card and select Update driver, and then choose Search automatically for updated driver software if an update is found, install it and restart your computer.

After updating, check if your videos play correctly.
Method 3: Reinstall Media Player or Reset Settings
Step 1 : Go to Start, open the Control Panel.
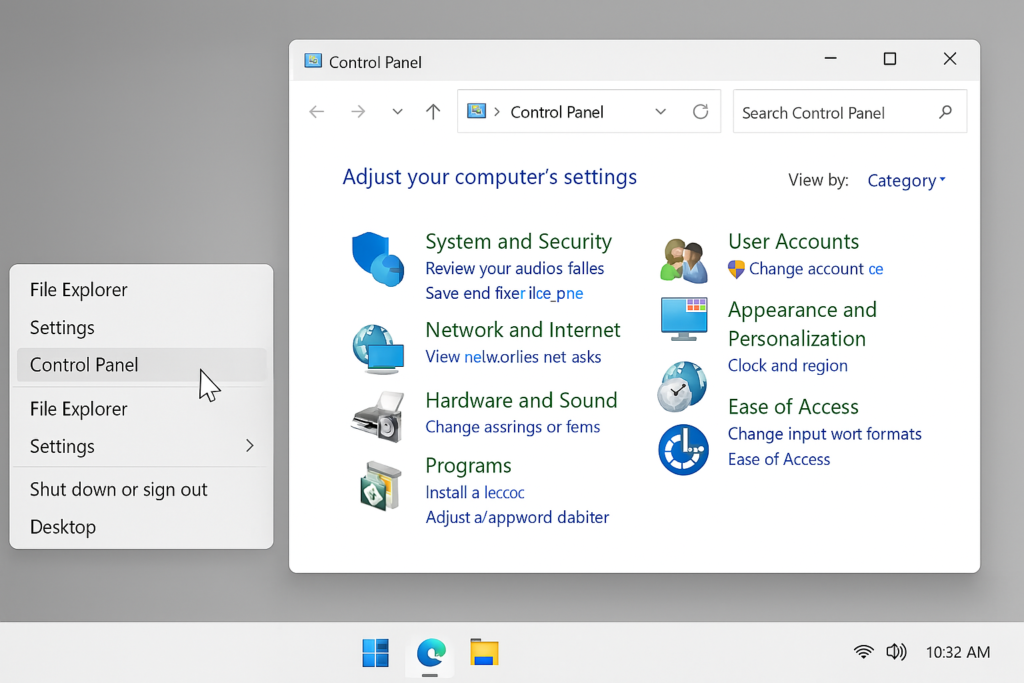
Step 2: Go to Programs then click on Programs and Features, find your media player (like Movies & TV or Windows Media Player) and Uninstall it, after uninstalling Reinstall the app from the Microsoft Store (for Movies & TV) or the official website (for Windows Media Player).
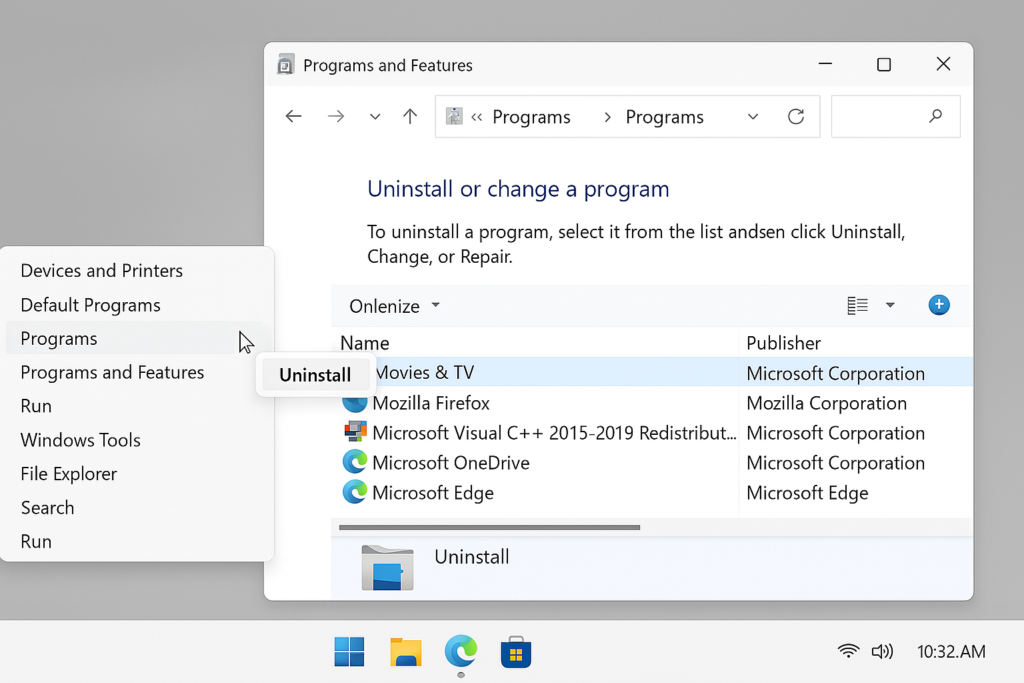
These are some methods to fix the video not playing issue in Windows.
How many types of codec are there?
The number of codecs is vast, and they evolve as technology progresses. The choice of codec depends on the use case, such as media streaming, file storage, or real-time communication, and the balance between compression efficiency and quality. There are several types of codecs used in various fields, each with its specific functions. Here are some common types of codecs:
- Audio Codecs:
- MP3 (MPEG Audio Layer III): One of the most popular audio codecs, used for compressing audio files while maintaining decent sound quality.
- AAC (Advanced Audio Coding): A more efficient codec than MP3, commonly used in streaming platforms and digital radio.
- FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec): A lossless codec that compresses audio without losing any quality, used by audiophiles and for archival purposes.
- WAV (Waveform Audio File Format): An uncompressed audio codec, commonly used for raw audio data.
- Opus: A codec designed for interactive speech and music transmission over the internet, offering low latency and high efficiency.
- Vorbis: An open-source codec used in applications like video games and streaming.
- Video Codecs:
- H.264 (AVC – Advanced Video Coding): One of the most widely used video codecs, especially for streaming and video recording.
- H.265 (HEVC – High-Efficiency Video Coding): A more advanced codec than H.264, offering better compression and quality, used in 4K video streaming.
- VP8/VP9: Video codecs developed by Google, used in YouTube streaming and web video (VP9 is the successor to VP8).
- AV1: A newer, open-source codec that aims to offer better compression and quality than both H.264 and HEVC, designed for high-resolution streaming.
- MPEG-2: An older video codec, primarily used for DVDs, Blu-rays, and broadcast television.
- Image Codecs:
- JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group): A widely used image codec for compressing photographic images, commonly used for web images.
- PNG (Portable Network Graphics): A lossless image format commonly used for images with transparency.
- GIF (Graphics Interchange Format): A lossless image format used for simple animations.
- WebP: A modern image codec developed by Google that provides better compression than JPEG while supporting both lossy and lossless formats.
- Container Codecs (Multimedia Codecs):
- MP4 (H.264 or HEVC): A multimedia container format commonly used for video and audio streaming or playback, often combined with H.264 or HEVC video and AAC or MP3 audio codecs.
- MKV (Matroska): A flexible multimedia container format that supports a wide range of codecs (including H.264, VP9, AAC, and more).
- AVI (Audio Video Interleave): A multimedia container that supports different video and audio codecs but is not as efficient as modern formats like MP4 or MKV.
- Streaming Codecs:
- RTSP (Real-Time Streaming Protocol): Used for streaming audio and video over the internet, often in surveillance or live streaming scenarios.
- WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communication): A set of standards and codecs used for real-time communication in web browsers, often used in video calls or conferences.
- Lossless vs. Lossy Codecs:
- Lossless Codecs: These codecs compress data without losing any information (e.g., FLAC, ALAC, PNG, and lossless H.265).
- Lossy Codecs: These codecs compress data by discarding some information, which may result in a loss of quality but achieves higher compression rates (e.g., MP3, AAC, H.264, and JPEG).
What are the common uses of Codec?
Here is the common uses of codecs:
- Codecs are used to compress and stream video content over the internet, making it possible to watch movies and TV shows online.
- Codecs are used to compress audio files, making them smaller and easier to share, stream, or download.
- Codecs are used in music production to compress and encode audio files, making it easier to share and collaborate on music projects.
- Codecs are used in the film and television industry to compress and encode video and audio files, making it easier to edit, distribute, and display content.
- Codecs are used in video conferencing software to compress and transmit video and audio data in real-time.
- Codecs are used in online meeting software to enable screen sharing, video, and audio communication.
- Codecs are used in virtual event software to enable live streaming, video playback, and audio communication.
- Codecs are used in online courses to compress and stream video lectures, tutorials, and other educational content.
- Codecs are used in e-learning platforms to enable the creation, distribution, and playback of educational content.
- Codecs are used in virtual classrooms to enable live streaming, video playback, and audio communication.
- Codecs are used in game development to compress and encode audio and video files, making it easier to distribute and play games.
- Codecs are used in game streaming services to compress and transmit video and audio data in real-time.
- Codecs are used in simulation software to enable the creation, distribution, and playback of simulated environments.
- Codecs are used in medical imaging to compress and encode image files, making it easier to store, transmit, and display medical images.
- Codecs are used in telemedicine to enable remote consultations, live streaming, and video playback.
- Codecs are used in medical research to enable the creation, distribution, and playback of medical research content.
- Codecs are used in surveillance systems to compress and encode video files, making it easier to store and transmit video footage.
- Codecs are used in security systems to enable the creation, distribution, and playback of security-related content.
- Codecs are used in advertising and marketing to enable the creation, distribution, and playback of promotional content.
What are the reasons behind the issue “Video Not Playing in Windows (Codec Not Supported, Need New Codec)?
Here are some common reasons behind the issue:
Missing or outdated codec: The codec required to play the video is not installed or is outdated. Media players such as VLC or Windows Media Player require regular updates to support new video and audio formats.
Incompatible codec: The codec used to compress the video is not compatible with the media player or Windows.
Corrupted codec: The codec is corrupted or damaged, preventing it from working properly.
Conflicting codecs: Multiple codecs are installed, causing conflicts and preventing the video from playing.
Outdated media player: The media player is outdated and does not support the required codec. Older versions of media players may lack support for newer codecs.
Windows updates: Windows updates may have removed or disabled the required codec.
Codec pack issues: Issues with codec packs, such as K-Lite or CCCP, can prevent videos from playing.
File format issues: Issues with the file format, such as a corrupted or incomplete file, can prevent the video from playing.
Driver issues: Outdated or corrupted graphics or sound drivers can prevent videos from playing.
System configuration issues: System configuration issues, such as incorrect registry settings, can prevent videos from playing.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, fixing video not playing issues on Windows can be achieved through a series of troubleshooting steps. By updating your video player, checking for codec issues, and ensuring that your graphics drivers are up-to-date, you can resolve many common video playback problems. Additionally, adjusting your system’s settings, such as disabling hardware acceleration or resetting Windows Media Player, can also help.
If the issue persists, consider using alternative media players or seeking further assistance from Microsoft support or online forums. By following these steps, you can enjoy smooth video playback on your Windows device. Regularly updating your system and software can also help prevent video playback issues in the future, ensuring a seamless viewing experience.